There are many reasons to test your business name, but this might be the most compelling: names can influence destiny.
Studies have linked a person’s first name with chosen career, company rank, even juvenile delinquency. For instance, one study claimed that if you are a woman with a gender-neutral name like Cameron, you may be more likely to succeed in a legal career. There’s even a fancy term for it: nominative determinism.
In business, shorter company names are usually more memorable and distinctive than long ones. And, as one blogger observed, IPOs may be more likely with a name under 13 characters. A name that begins towards the start of the alphabet might place you towards the top in local or online lists.
How to come up with a business name
Start by surveying the marketplace. Which memorable business names do you like, and which ones miss the mark? Look at your favorite restaurants or coffee shops; think of catchy organizational names.
Ask yourself what you hope your company name will ultimately convey. For example, do you want to seem approachable, trustworthy, family-oriented? How can words and phrases help you reach that goal?
Make a long list of potential names — don’t edit yourself at first. Solicit help from colleagues or even take a look at naming services. Do your research to confirm that your name is unique and isn’t likely to confuse consumers or land you in court against an established brand.
Once you think you’ve hit on a few good potential names, write them out to see how they look. Say them aloud to hear how they sound.
Your business name can be evocative of the kinds of client you serve, your company mission, or what makes your business unique. No matter what imagery your company name is associated with, however, one thing is certain: your name is your calling card.
It’s no wonder Fortune 500 companies spend millions of dollars on brand name testing methodology, studies, and consultants when it comes time to name a business. But here’s the good news: you don’t need millions of dollars to run a successful test, and you don’t need a thousand company name ideas to begin testing. Follow these six tips and you’ll be well on your way to finding the best name for your company.
1. When testing company names, only test one thing at a time
Your business name is distinct from your business logo, and creating the two should be separate processes. Each has different considerations and will be judged using distinct criteria.
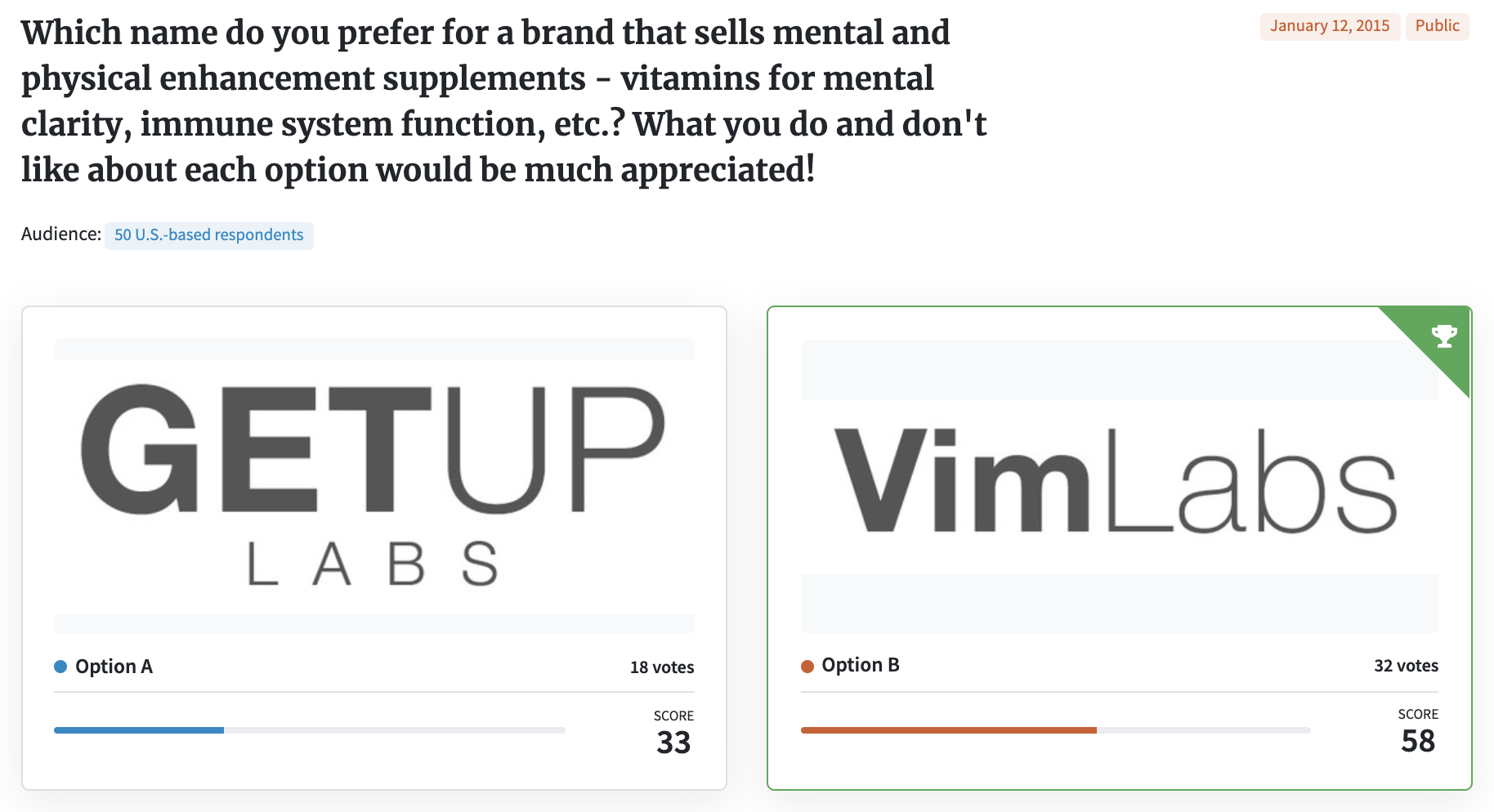
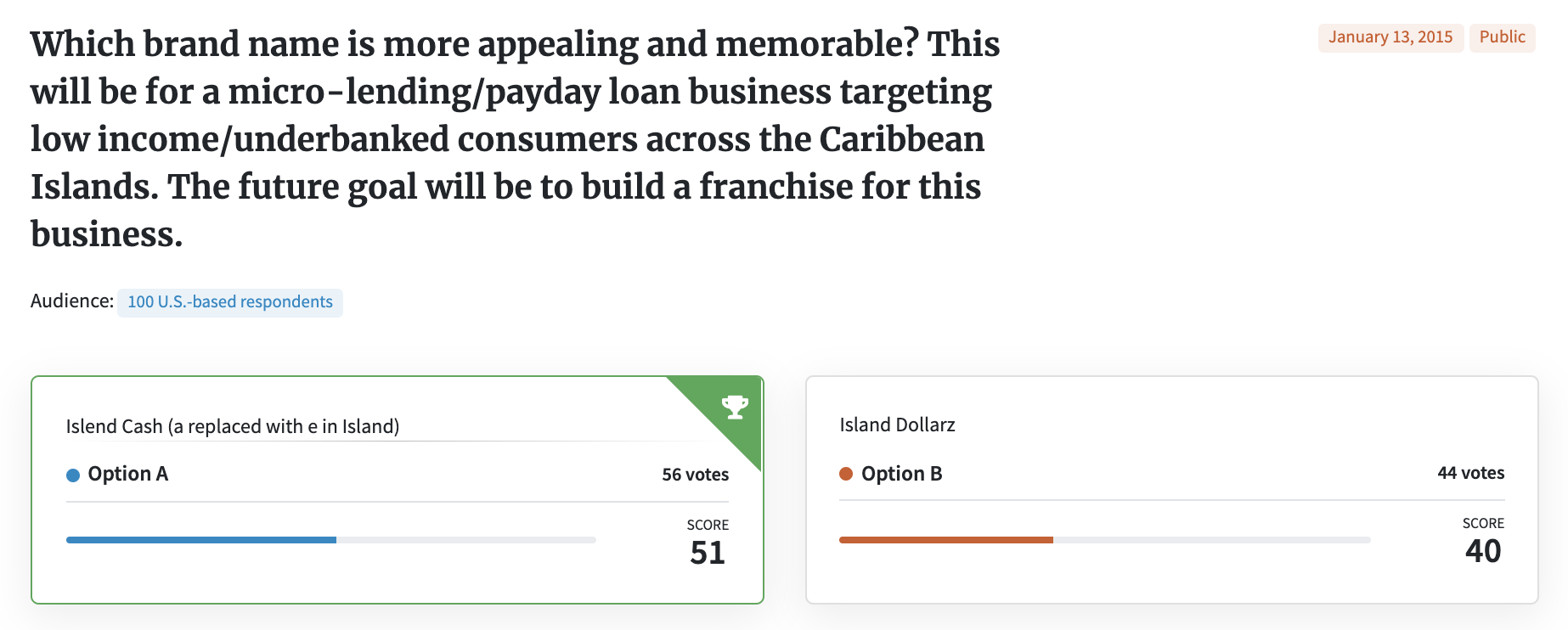
Testing more than one thing at a time is also problematic because it skews your results. Below is an example where an entrepreneur wanted to test two business names. However, when he posed the question, he submitted the names in two different type treatments that some saw as a logo concept. Respondents in this PickFu poll commented on both the name and the design. Sounds like twice the value, right? Wrong.
This is a type of polling bias called a double-barreled question. A double-barreled question asks two separate things but only leaves room for one answer. Respondents usually only respond to the one that means the most to them. And even if the respondent only reacted to the name in a written comment, that reaction was likely subconsciously influenced by the logo and vice versa.
Some responses that reference the name:
• “I chose ‘Get Up,’ because Vim is entirely foreign to me as a company name/product name. Get Up makes me think of the things I may be able to achieve with this product.”
• “[Vim] sounds like it might have to do with vitamins. The other would lead me to believe it was a male enhancement product.”
Some responses that reference the logo:
• “[Option B has a] cleaner look and name.”
• “[Option A] has an appealing font and name.”
When testing your business name, test your business name only. Leave the logo design and any other considerations for later tests.
Read more about double-barreled questions and writing unbiased questions here, and when you’re ready, get our tips for testing logos here.
2. Explain a little about the business as you test company names
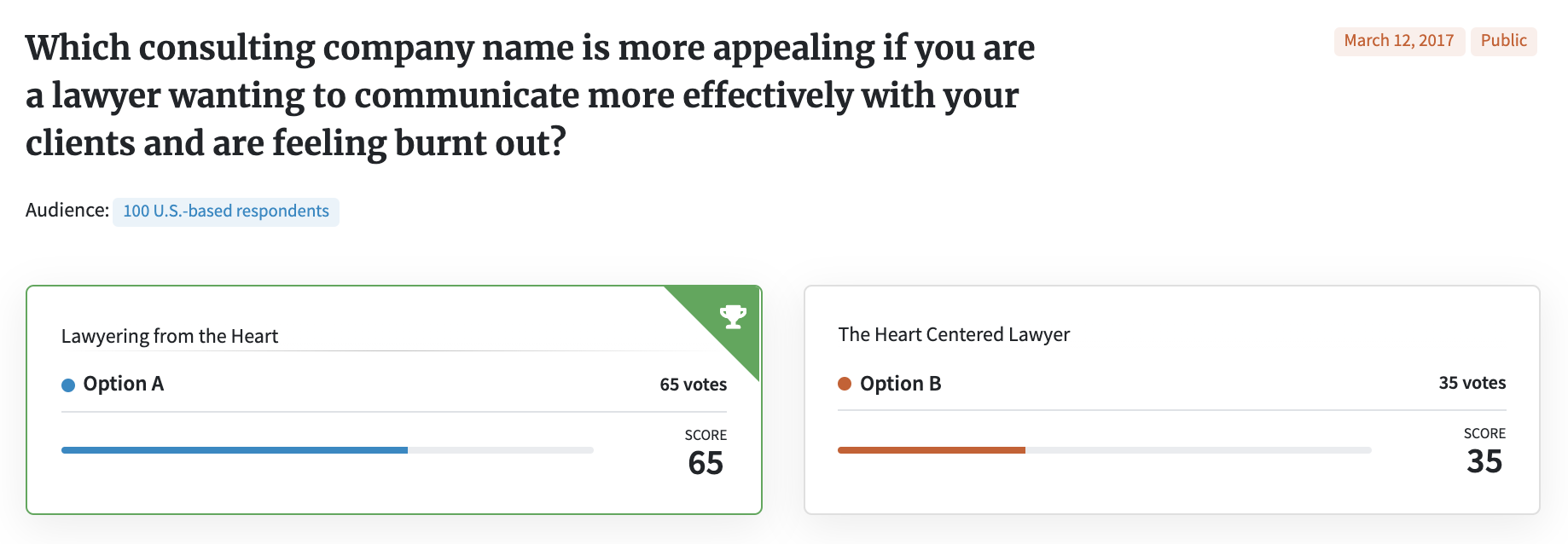
Unless it’s obvious what your business does (for instance, John’s Insurance Company), it’s usually a good idea to briefly state your company’s purpose. Here’s a good example:
Without a little context to explain what the consultancy does, the idea of hearts and lawyers might seem an odd pair. A quick, simple explanation will help respondents understand what your business name seeks to accomplish.
Here’s another example:
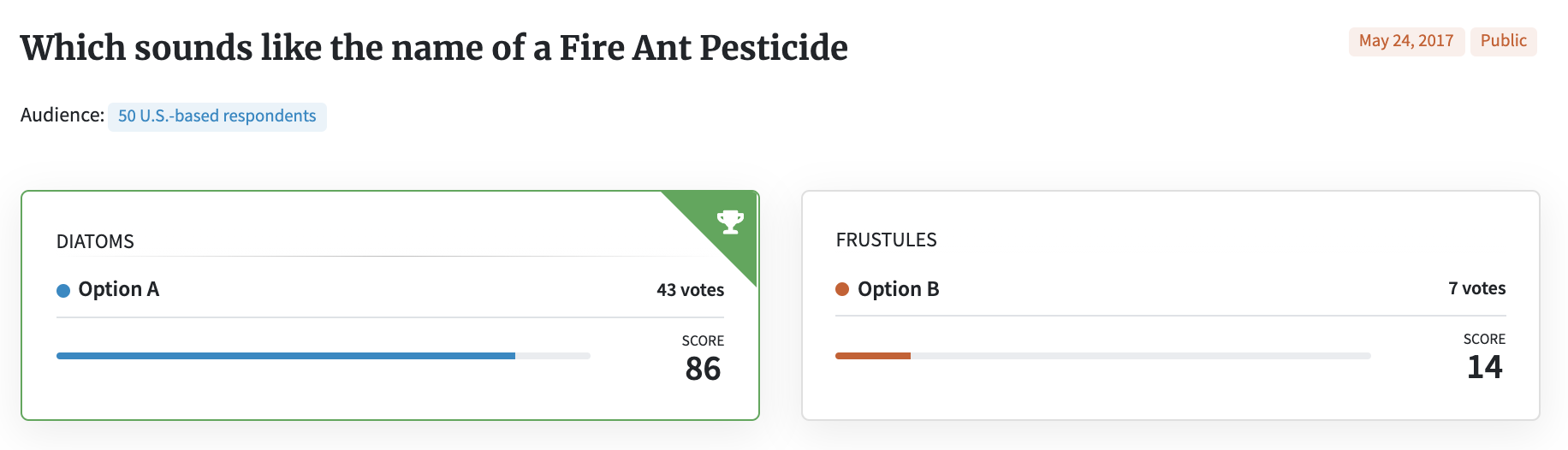
In this brand name testing example, because respondents know what the product does, they can give helpful answers like these:
• “[Option B] sounds like a snack for humans.”
• “Frustules doesn’t sound appealing. Frustules sounds like a part of a body (I think it’s because of the -ules ending).”
• “DIATOMS sounds like a substance that will kill insects when you say the name aloud. It sounds powerful, simple, and to-the-point.”
• “[Option A] totally sounds like a bomb for bugs”
In my last post, I mentioned that sometimes in logo tests it’s valuable to ask a blind question, without any background on your company. This will help you understand what kind of company respondents believe the logo design would fit. There are instances where this could also be useful with business name tests, too. For instance, if the pollster above decided he wanted to name his product Frustules after all, a good question without context might be, “What kind of product does the name Frustules sound like to you?” Still, more often than not, it makes sense to tell people what you do.
3. Test the pronounceability and misspellings of business names
Names whose pronunciations aren’t obvious aren’t necessarily bad. There’s a band whose name is !!! (pronounced chk-chk-chk) that has released seven albums. And ice cream brand Häagen-Dazs invented its name entirely to be “Danish-sounding,” even though true Danish never uses an umlaut (the accent over the a) and would never put the letters z and s next to each other.
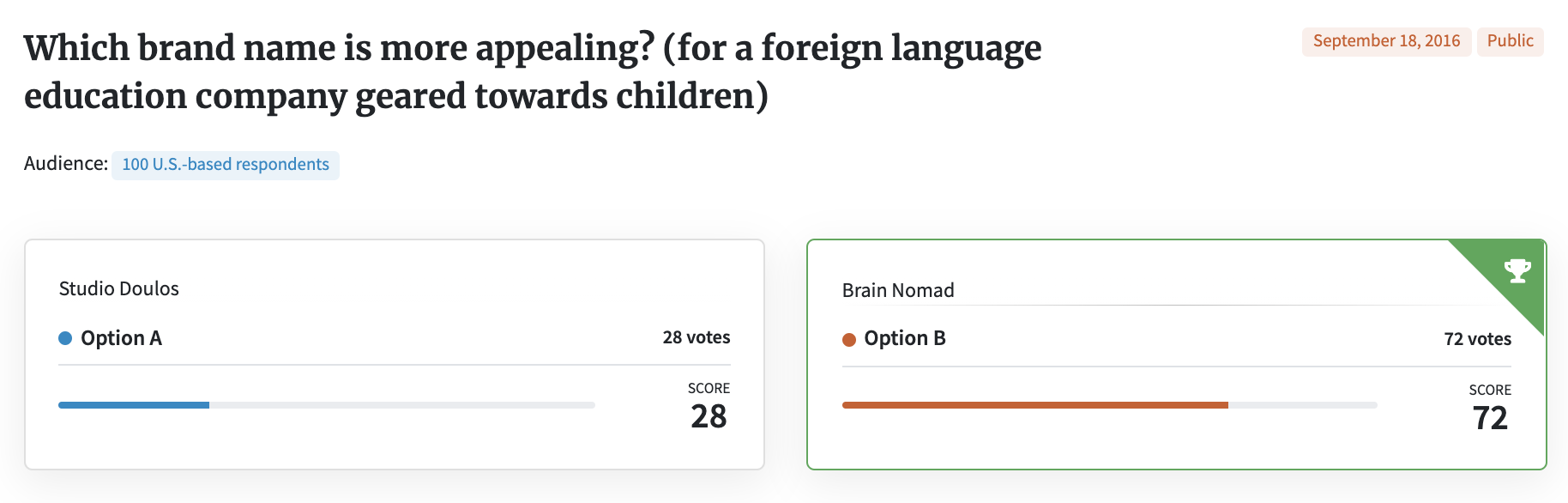
But not knowing how to pronounce something can also be a turn-off to customers. Here’s an example where a customer tested two brand names.
72% chose Option B, and the pronunciation was a big reason why:
• “The first one seems hard to say/pronounce”
• “[Option B] is easier to pronounce.”
• “Choice B is simpler to remember and pronounce. Any person who has heard of the company will remember the name easier in order to tell others about it or ask others if they’ve tried it.”
• “Option B is easier to process and pronounce.”
Just like there are exceptions to the pronunciation rule, there are good and bad misspelled company names, too. Google is a misspelling of the word googol, which is the number ten to the one-hundredth power, a reference to the many search results that Google delivers. Lyft is a misspelling of lift, as in “catching a lift.” But other misspellings can seem accidental or just be offputting. One brand that always bothers me is “Unstopables,” a line of laundry detergent made by Downy. The word unstoppable has two Ps, but Downy only uses one. Was it a mistake? Maybe not, but it sure looks that way!
Below is an example of why you should always test intentionally misspelled names. Here, both names contain misspellings, but the first came across as a clever play on words, while the second seemed to cheapen the brand in the eyes of those polled:
So, if your name idea is potentially difficult to pronounce or includes a misspelling, always, ALWAYS be sure to test it. It may work in your favor, or it may work against you, but you’ll want to know. Test company names before you launch.
4. Once you’ve tested a business name, test an accompanying tagline
As mentioned in Tip #1, you should only test one thing at a time. But once you’ve settled on a name (or at least narrowed it down to a few finalists), it makes sense to run additional tests in order to see if your company’s tagline flows alongside it.
Your tagline can express what makes your business unique or give information about what you do. This is where you would want to exclude information about your company. Let’s take a situation like the lawyer’s poll from Tip #2. If the business owner decided the business’s name should be Lawyering From The Heart, she then might want to see if a tagline clarifies what the name means. She might ask a poll like, “Given these taglines, which do you feel connects to you more?” and offer options like “Lawyering From The Heart: Help out, don’t burn out” or “Lawyering From The Heart: Encouraging stronger client communication,” and see how people react. Is the tagline clear? Is it confusing? Without context, what do respondents think the consultancy does?
Read this post about testing marketing messages to help you develop your next tagline, then try it out on PickFu today.
5. Test your business name with the logo
You’ve tested and whittled down your business names to a few contenders — or maybe just one. Now’s the time to test the name with the accompanying logo.
Ideally, you’ll have tested your logo separately. You might have gotten feedback at that point to help refine not only the design of the logo but also your company name.
By testing the name and logo together as a final or close-to-final step, you’ll determine whether the name makes sense to consumers and that you didn’t create a bad logo.
If you’re stuck between two names but you’re confident about the logo, put the names with the final logo in a head-to-head poll, as this business owner did in the example below. If you think you’ve landed on a winning combination, pose an open-ended question for the most comprehensive feedback.
6. Dig into the data and test again
Take the time to break down the data at each round of testing, not just when you think you’re close to the finish line. Look at the key demographics of respondents that make sense for your business or product to understand why they voted the way they did and what drew them to or turned them off of your company name. If necessary, test again — and again.
The earlier in the process you gather and use this feedback to land on the best name for your business, the more likely that name will stick with actual customers.
Frequently asked questions about company names
Yes. Generally, they involve puns. For example, a salon might be called Curl Up & Dye or Julius Scissors. Puns might garner a chuckle or eye roll, but you have to consider whether customers want to do business with a company that has a gimmicky name (it works better in some industries than others). Again, this is why testing company names is important!
Split test the names in a PickFu poll, but be sure that you test only the names, not any accompanying logos, at least initially. Choose an audience that matches your target customer and use their feedback to decide on the best name.
Think of any iconic brand, like Nike, Coca-Cola, or Amazon. The images that these brands evoke are not only based on their business name, but also company history, iconography, and prominence in our daily lives. Similarly, as you ideate business names, remember that a name alone won’t create a brand — you have to present your business a certain way, operate it a certain way, and continually reinforce that brand image in order to make an impression.
No one knows your company better than you do, but if you’re struggling to come up with name ideas, there are companies and consultants you can hire to do this for you. When you find someone with a lot of history naming companies, you’ll feel confident they’ll create a list of good organization names for you to consider. Once you test some of those names using PickFu, you’ll be even more confident your LLC name ideas are resonating.
Mobile app names are an incredible marketing asset in the App Store. Refer to this guide on naming mobile apps, and be sure to test your mobile app business names using PickFu before you launch.
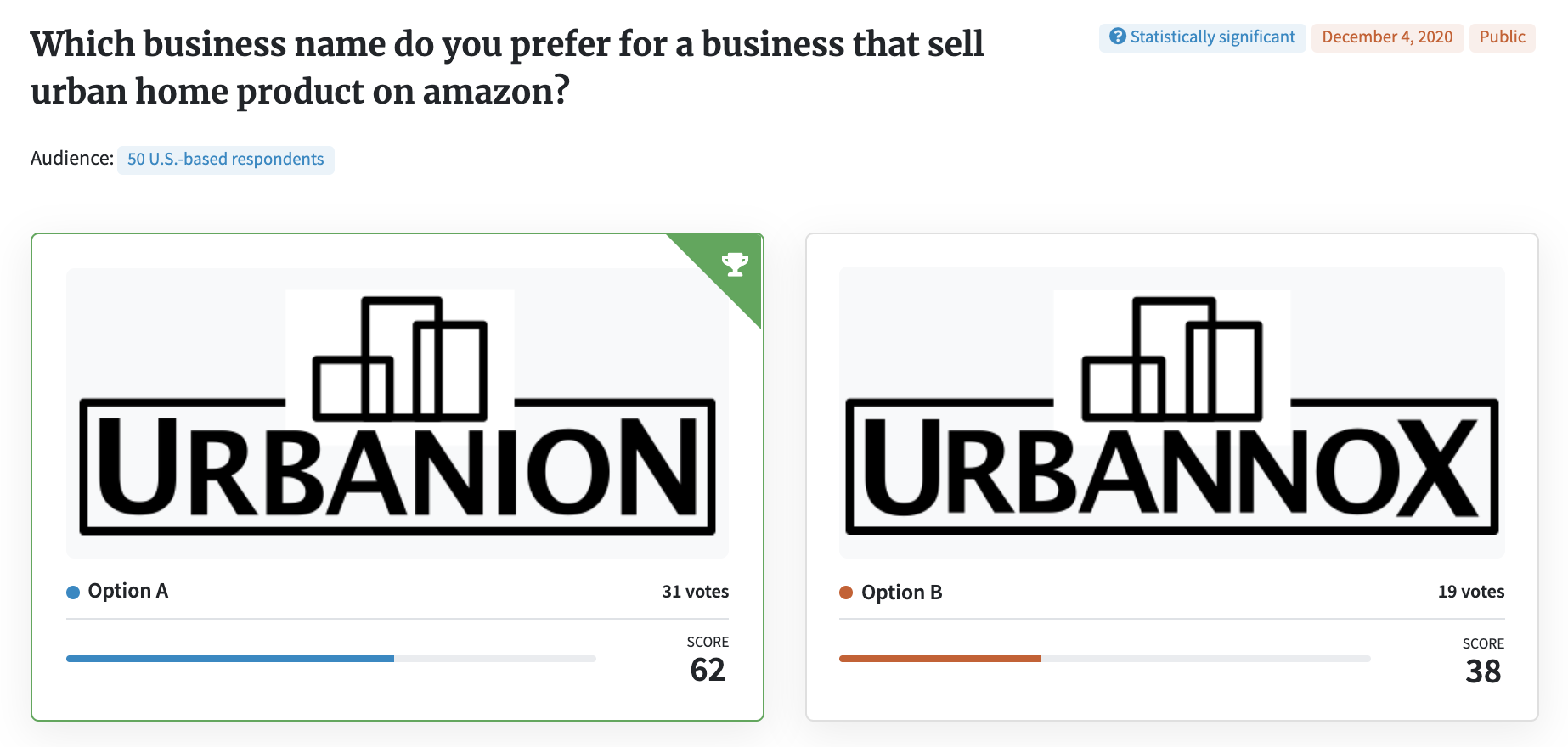
Your e-commerce store should be a destination for shoppers, so you’ll need a store name they’ll want to visit again and again. Check out this example of how a seller tested an e-commerce store name using PickFu. Then, think about your own name ideas. If you’re struggling to come up with good ones (and don’t forget, you’ll also need the URL to be available), hire a naming company or consultant.
Need to choose a name for your business? Run a PickFu poll.